Tropical Storm Dexter: 2025 Atlantic Hurricane Season Updates
Tropical Storm Dexter, the fourth named storm of the 2025 Atlantic hurricane season, has captured attention as it navigates the western Atlantic. Forming on August 3, 2025, off the coast of North Carolina, Dexter marks a notable entry in a season that has been quieter than anticipated but is showing signs of intensification as August progresses. This article compiles all available updates on Tropical Storm Dexter, its path, impacts, and potential developments, drawing from reports by the National Hurricane Center (NHC), AccuWeather, and other meteorological sources.
Formation and Current Status
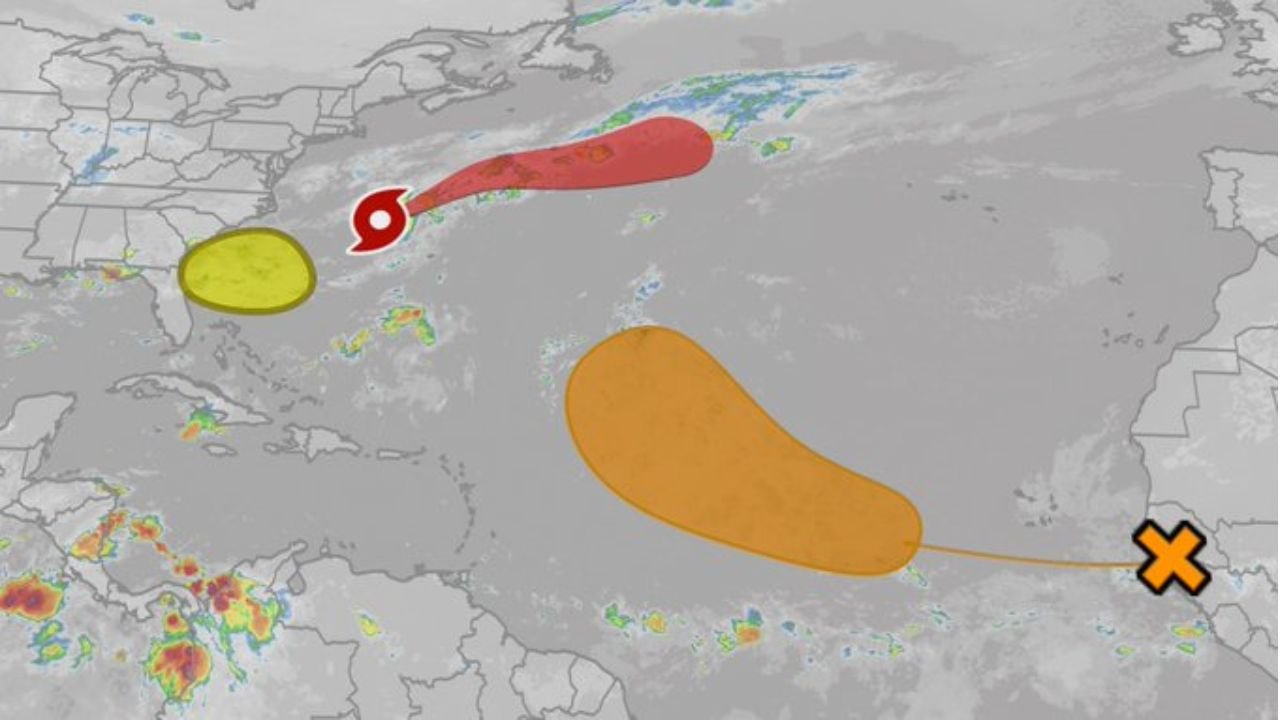
Tropical Storm Dexter officially formed late Sunday, August 3, 2025, from a low-pressure system along a stalled frontal boundary a few hundred miles east of North Carolina’s Outer Banks and approximately 300 miles west-northwest of Bermuda. By 11 p.m. AST on August 4, 2025, the NHC reported Dexter’s center at latitude 36.8°N, longitude 65.6°W, about 315 miles north of Bermuda, moving northeast at 13 mph with maximum sustained winds of 45 mph and a central pressure of 1002 mb. The storm’s cloud pattern is described as ragged, with deep convection displaced east of its low-level center due to strong westerly wind shear of about 20 knots, expected to increase to over 30 knots by Monday night.
Dexter is classified as a “fish storm,” posing no immediate threat to land as it tracks away from the U.S. East Coast and north of Bermuda. The NHC predicts slight strengthening, with winds potentially reaching 50 mph by Tuesday, August 5, before Dexter transitions into a post-tropical or extratropical cyclone by Wednesday or Thursday, August 6 or 7, due to high wind shear and dry air.

Earlier Development: Invest 93L
Before becoming Tropical Storm Dexter, the system was tracked as Invest 93L, a disturbance off Florida’s east coast starting around July 13, 2025. The NHC initially gave it a 10% chance of cyclone formation on July 14, which increased to 40% by July 15 and then dropped to 30% by July 17 as the system became disorganized. Invest 93L moved westward across Florida, bringing heavy rainfall (4-8 inches) and flash flooding risks to the Florida Peninsula, southern Louisiana, southwestern Mississippi, and eastern Texas. Despite favorable conditions in the Gulf of America (formerly Gulf of Mexico), the system moved inland over southeastern Louisiana by July 17, reducing its chances of developing into a named storm at that time.
Meteorologists, including AccuWeather’s Alex DaSilva and Dylan Federico, noted the potential for Invest 93L to become Tropical Storm Dexter if it had remained offshore longer. Spaghetti models indicated a westward track toward Louisiana, with a possible northward shift into the Mississippi Valley. However, the system’s inland movement and disorganized structure limited its development. The primary concern was heavy rainfall, with coastal Louisiana expecting up to 4-8 inches, posing significant flash flooding risks.
Context of the 2025 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 2025 Atlantic hurricane season, running from June 1 to November 30, has seen three named storms prior to Dexter: Andrea, Barry, and Chantal. Chantal, which formed on July 5, brought heavy rain and flooding to North Carolina. Historically, the fourth named storm typically forms around August 15, making Dexter’s formation on August 3 slightly ahead of schedule. The first hurricane of the season usually occurs around August 11, but as of August 5, no hurricanes have formed in 2025, potentially marking a delay from the average.
Despite early predictions of an above-average season, with NOAA forecasting 13-19 named storms, recent updates from Colorado State University suggest a slightly above-normal season with up to 16 named storms, eight hurricanes, and three major hurricanes. Factors such as cooler Caribbean waters and elevated wind shear have tempered storm intensity, particularly in regions typically associated with powerful hurricanes. Dexter’s formation in warmer-than-average waters (29°C, about 1.5°C above normal) highlights the influence of climate change, which has made such ocean temperatures 400 times more likely, according to Climate Central’s Ocean Shift Index.

Impacts and Precautions
While Tropical Storm Dexter is not expected to make landfall in the U.S., its earlier iteration as Invest 93L caused significant rainfall across Florida and the Gulf Coast. The system’s current path suggests minimal direct impact, but high surf and dangerous rip currents are possible along the U.S. East Coast and into Canada’s maritime provinces. Marine interests should remain vigilant due to Dexter’s tropical storm-force winds extending up to 115 miles from its center.
Residents in vulnerable regions are urged to stay informed through NHC and NOAA updates, prepare emergency kits, secure homes, and develop evacuation plans. Businesses should establish continuity plans and coordinate with local officials. The NHC is also monitoring two additional systems: a tropical wave off Africa with a 50% chance of becoming a tropical depression and a low-pressure area off the southeastern U.S. coast with a 30% chance of development, which could enter the Gulf of America but is unlikely to affect the western Gulf Coast.
The Name Dexter
Dexter is a new name on the 2025 Atlantic hurricane list, replacing Dorian, which was retired after the devastating Category 5 Hurricane Dorian struck the Bahamas in 2019, causing 74 deaths and $4.6 billion in damage. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) selects names to be culturally relevant and easy to pronounce, and Dexter, meaning “right-handed” or “skillful” in Latin, makes its debut this year.
Forecast and Future Outlook
The NHC’s latest advisory on August 4, 2025, indicates Dexter will maintain its current strength or slightly intensify before transitioning into a post-tropical system by midweek. Its northeastward trajectory keeps it over open waters, reducing land-based impacts. However, the Atlantic hurricane season is entering its peak period (mid-August to mid-October), with increasing sea surface temperatures and decreasing wind shear likely to fuel more tropical activity. The next named storm, if it forms, will be Erin.
Conclusion
Tropical Storm Dexter, while not a significant threat to land, underscores the dynamic nature of the 2025 Atlantic hurricane season. Its formation from Invest 93L and subsequent path highlight the importance of continuous monitoring and preparedness, especially as the season approaches its most active phase. Residents along the U.S. East Coast and Gulf Coast should remain vigilant, as even non-landfalling storms can cause indirect impacts like flooding and rip currents. Stay updated through trusted sources like the NHC, NOAA, and local meteorological services to ensure safety and preparedness.













Post Comment